Chronic Fatigue Supplements: What Science Actually Says
Chronic fatigue syndrome, also called ME/CFS, impacts millions of lives around the world. People with this condition often find everyday activities incredibly difficult.
The lack of FDA-approved treatments leads many patients to try supplements. But is there good evidence that these supplements help?
This guide looks at the science behind supplements for chronic fatigue, giving you clear facts without exaggerated claims.
While supplements may help manage symptoms, they’re not a cure for ME/CFS. Always work with healthcare providers familiar with your condition for a comprehensive treatment plan.
Key Takeaways
- CoQ10 combined with NADH shows the strongest evidence for reducing fatigue in ME/CFS patients
- Mitochondrial support supplements (NAD+ precursors, L-carnitine) may address energy production issues at the cellular level
- Research quality is generally low to moderate with small sample sizes and methodological limitations
- Response to supplements varies widely between individuals, highlighting the need for personalized approaches
What is Chronic Fatigue Syndrome?
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) has several key symptoms:
- Unexplained, persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest
- Post-exertional malaise (worsening of symptoms after physical or mental effort)
- Unrefreshing sleep
- Cognitive impairment (often called “brain fog“)
- Orthostatic intolerance (symptoms that worsen when standing up)
Despite affecting millions worldwide, the cause is unknown. Researchers have proposed several theories:
- Immune dysfunction
- Mitochondrial problems
- Infectious triggers
- Oxidative stress
- Neuroendocrine imbalances
Why Many Turn to Supplements
Since there are no FDA approved treatments for ME/CFS, 35-68% of patients use nutritional supplements to try to reduce their symptoms.1
Current treatments mainly manage symptoms, with less than 5% of patients ever getting back to their pre-illness activity levels.2
This gap in treatment has led patients and researchers to look for alternatives that address the various physiological pathways involved in the condition.
Supplement Safety Note
Supplements receive minimal FDA regulation and may not be safe for everyone. They can interact with medications and other supplements. Always consult your doctor before starting any supplement regimen.
Most Promising Supplements for Chronic Fatigue

People with chronic fatigue syndrome may find relief through certain supplements. Here’s what research shows about the most promising options for improving energy levels.
1. CoQ10 and NADH: The Top Contenders
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydride (NADH) stand out as some of the most promising supplements for patients with chronic fatigue syndrome.
Multiple studies show positive results when these supplements are used together. Researchers found that taking CoQ10 (200 mg daily) with NADH (20 mg daily) significantly reduced fatigue in ME/CFS patients over 2-3 months.3
In the study with 73 participants, this combination lowered maximum heart rate during exercise tests and reduced how tired patients felt at each check-up.4
Research reviews have consistently found that CoQ10 reduces fatigue, especially when paired with NADH, though many studies have been relatively small.5
Why they help: Both supplements are key players in how cells produce energy through mitochondrial processes, potentially improving the reduced energy production seen in ME/CFS patients.
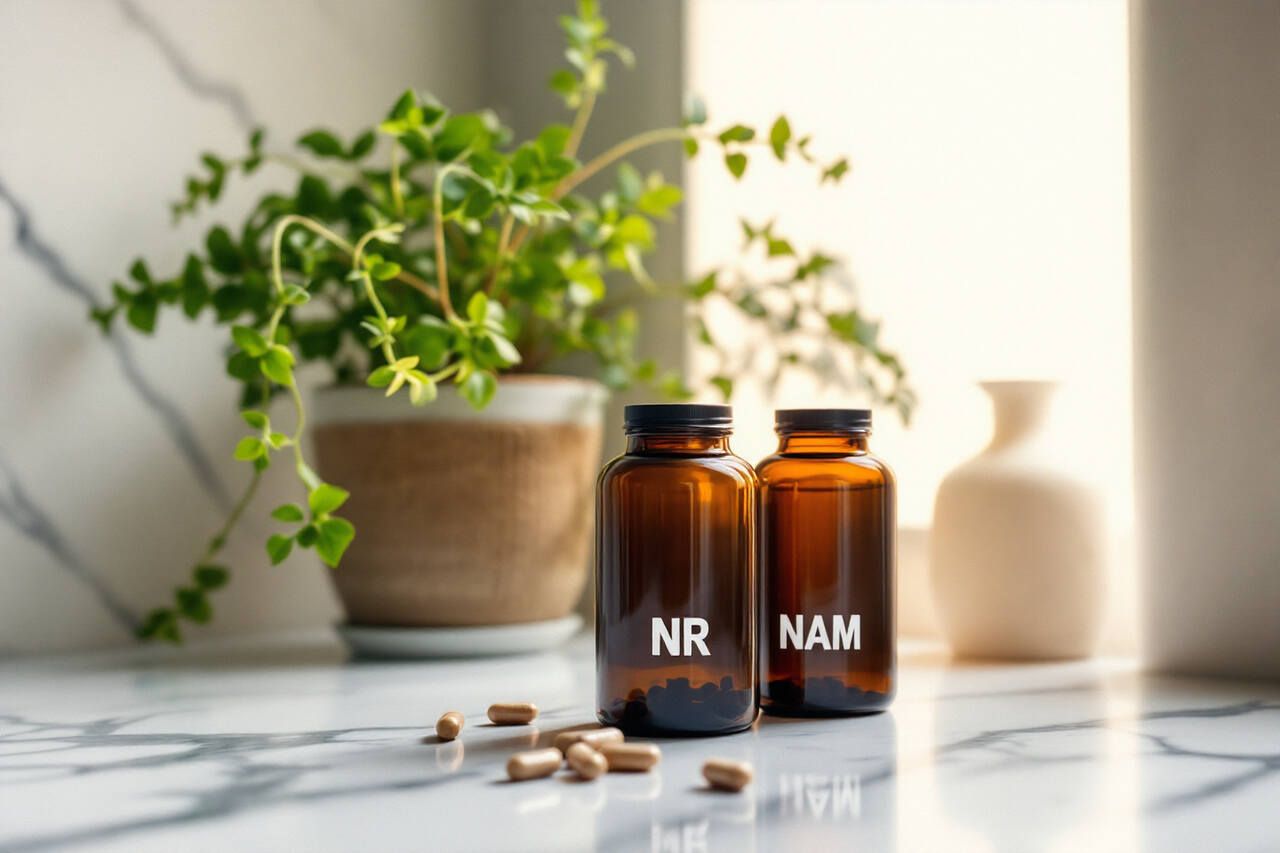
2. NAD+ and Its Precursors
NAD+ is an essential coenzyme that exists in all living cells. It’s important for many biological functions, including how your body creates energy, repairs DNA damage, regulates genes, and sends calcium signals.
In the electron transport chain, NAD+ helps transform nutrients into ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, which is how cells generate energy.
Studies show that NAD+ decreases with aging and in various diseases. This reduction may cause lower energy levels and impaired cell function.6
Clinical Evidence:
- A review of clinical research examined if NAD+ and NADH supplements help people with various conditions, including CFS. Looking at ten studies with 489 participants, researchers found that those with CFS experienced less intense fatigue, better sleep quality, and improved overall wellbeing.7
- A study by Forsyth and colleagues found that CFS patients who took 10 mg of NADH daily for four weeks experienced significant relief from fatigue symptoms.8
NMN and NR (nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinamide riboside) are drawing interest as possible CFS treatments. Unlike direct NAD+ supplements, these precursor compounds are better absorbed and more effectively transported into cells, resulting in higher NAD+ levels.
By improving NAD+ metabolism, these compounds might help repair the kynurenine pathway, which scientists believe is involved in ME/CFS.9
3. L-carnitine: Mixed But Promising Results
L-carnitine moves fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production. Research shows it might help with fatigue, but results vary.
In a key 2004 study by Vermeulen and colleagues, 90 chronic fatigue syndrome patients took either acetyl-L-carnitine (2 grams daily), propionyl-L-carnitine (2 grams daily), or both for 24 weeks.10
The acetyl form improved mental tiredness, while the propionyl form reduced overall fatigue.
Another study with older adults found that acetyl-L-carnitine lowered both physical and mental fatigue and boosted brain function and daily activities.11
Not all research agrees, though. Larger studies, particularly those on cancer-related fatigue, show inconsistent benefits, suggesting that more condition-specific studies are needed.
4. Creatine: Supporting Brain Energy
Research has identified low levels of creatine in brain areas relevant to CFS symptoms, including regions involved in cognition and energy regulation.12
In a recent study, CFS patients took creatine supplements for six weeks. Patients experienced reduction in fatigue, better reaction time on cognitive tests, and stronger grip strength.13
Another study looked at creatine for post-COVID-19 fatigue, which is similar to CFS. After six months, participants had more creatine in several brain regions and muscles, along with less fatigue and improvements in breathing, body pain, headaches, and concentration.14
Safety and Dosing: Creatine supplementation appears generally well-tolerated in CFS patients. Typical dosing protocols include a loading phase of approximately 16g daily, followed by a maintenance dose of 3-5g daily.
To better understand how creatine may support brain health, see our detailed article covering the nootropic properties of creatine.
5. Oxaloacetate: Promising But Preliminary
Oxaloacetate is a newer supplement with promising early results.
A small study of 52 ME/CFS patients found that oxaloacetate reduced fatigue in 80% of participants. Some people reported up to 80% less fatigue.15
Higher doses (1000 mg three times daily) worked better than lower doses, suggesting the effect depends on the amount taken.
Oxaloacetate helps the Krebs cycle, which supports cellular energy production. While these results were described as “striking and surprising,” larger controlled studies are needed to confirm the findings.
6. Vitamins and Minerals: Mixed Evidence
Research on vitamins and minerals for ME/CFS shows mixed results:
- Vitamin D may help with general fatigue, but there’s limited evidence specifically for ME/CFS patients. One study found that vitamin D supplements improved fatigue symptoms in people with stable chronic conditions.16
- Vitamin C (500 mg daily) significantly reduced fatigue in obese adults during a small controlled trial, but studies focusing on ME/CFS patients are still needed.17
- Zinc supplements (30 mg daily for 70 days) reduced fatigue in elderly people and increased their zinc blood levels.18 Another study is currently testing if zinc combined with melatonin helps ME/CFS symptoms.19
- B vitamins, especially thiamine (B1), have shown promise in reducing chronic fatigue in patients with multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Sulbutiamine, a man-made form of thiamine, significantly decreased fatigue scores in multiple sclerosis patients.20
- A research review found ME/CFS patients had lower vitamin E levels than healthy individuals, though this finding disappeared when analyzing only the most reliable studies.1 More research on vitamin E supplementation is needed.
7. Melatonin and Zinc: Ongoing Research
A new clinical trial is testing “MelatoZinc,” which combines melatonin (1 mg) and zinc (10 mg) as a potential treatment for ME/CFS.19
This carefully designed study will compare the supplement to a placebo in 106 patients who have ME/CFS according to official 2011 guidelines. Researchers will measure if the supplement reduces fatigue and is safe to use.
Scientists believe this combination might help because melatonin helps control sleep cycles, while zinc supports immune function and manages oxidative stress. Both of these processes may be involved in ME/CFS.
8. Panax Ginseng: Limited Evidence
Panax Ginseng has been used traditionally to combat fatigue, with research confirming these effects.21 The herb likely helps by enhancing how the body processes energy and through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities. Research specifically examining its effects on ME/CFS is still limited.
How Nutritional Supplements May Work

Several plausible mechanisms may explain why certain dietary supplements show benefits in ME/CFS:
- Boosting Mitochondrial Function: People with ME/CFS often have problems with their mitochondria making enough ATP. Many mitochondrial health supplements support energy production.
- Reducing Oxidative Stress: Studies show oxidative stress contributes to ME/CFS. Antioxidant supplements including CoQ10 and vitamins C and E may lower oxidative damage and related symptoms.
- Balancing Immune Function: Immune dysregulation is a proposed mechanism in ME/CFS. Certain supplements (zinc, vitamin D, some herbal preparations) may help normalize immune function and reduce inflammatory markers.
Safe Supplement Use for Chronic Fatigue Relief
When you have chronic fatigue, supplements can help but safety always comes first. Before adding any supplements to your chronic fatigue plan, consult with a healthcare provider who knows your medical history.
Consider these safety guidelines when adding supplements to manage chronic fatigue:
- Start with one supplement and use it for 2-3 weeks before adding another. Fatigue symptoms can fluctuate so give each supplement time to see what it does.
- Start with half the recommended dose on the label especially if you’re sensitive to medications or have multiple health conditions. You can increase to full dose if needed and tolerated.
- Take supplements with the same meal every day to establish routine and help you track changes in your energy levels or symptoms.
- Keep a symptom journal of your fatigue levels, other symptoms and when you take supplements. This will help you identify patterns and see which supplements are working for you.
- Be patient. Some supplements that support energy production and reduce fatigue may take weeks to show benefits. Quick fixes are rare with chronic fatigue and sustainable improvements take time.
Because ME/CFS affects everyone differently, personalized treatment of chronic fatigue works best. When possible, supplements should target specific deficiencies.
Testing to Guide Supplementation
While general supplement recommendations are helpful, personalized testing is more targeted for ME/CFS patients. Functional testing helps identify specific deficiencies and imbalances that may be contributing to your symptoms.
Key benefits of testing before supplementation:
- Establish a baseline to track progress over time
- Avoid unnecessary supplements that may not address your specific needs
- Optimize dosages based on your biochemistry
For people with chronic fatigue, comprehensive biomarker testing that looks at multiple systems can be valuable. Jinfiniti’s AgingSOS® Advanced Longevity Panel looks at all the interconnected systems that impact energy production and cellular health, including mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, inflammation and micronutrient status – all of which are involved in ME/CFS.
This type of testing gives you and your healthcare provider actionable information to develop a more precise supplementation strategy, potentially improving outcomes and reducing trial and error.
Remember to always interpret test results with a knowledgeable healthcare provider who understands ME/CFS.
When to Seek Help for Chronic Fatigue
Chronic fatigue requires medical attention when it significantly impacts your daily life.
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Fatigue that persists for six months or longer despite adequate rest
- Extreme exhaustion after physical or mental activities that previously caused no issues
- Unrefreshing sleep or worsening fatigue despite increasing rest
- New symptoms like joint pain, cognitive difficulties, or recurring sore throat
- Depression, anxiety, or mood changes accompanying your fatigue
- Fatigue that prevents you from fulfilling work, family, or social responsibilities
Early intervention can lead to more effective management strategies and help identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to your symptoms.
For additional support and information, visit trusted resources such as the CDC ME/CFS Patient Toolkit, the Solve ME/CFS Initiative, or the Bateman Horne Center to better understand your symptoms and prepare for medical appointments.
Supportive Lifestyle Practices
Beyond supplements, these lifestyle approaches can help manage chronic fatigue:
- Gentle, consistent movement: Light exercise like walking, swimming, or yoga can gradually improve energy levels when practiced regularly but without pushing to exhaustion
- Energy pacing: Planning activities around your energy levels and taking rest breaks before becoming completely depleted
- Sleep hygiene: Maintaining consistent sleep and wake times, creating a restful bedroom environment, and limiting screen time before bed
- Stress management: Incorporating mindfulness, meditation, or breathing exercises to reduce the energy-draining effects of chronic stress
- Nutrition focus: Emphasizing nutrient-dense whole foods that provide sustained energy while limiting processed foods, caffeine and alcohol that can worsen fatigue patterns
These foundational practices create a supportive framework that can enhance the effectiveness of any supplements you add to your routine.

Limitations of Supplements for ME/CFS
Research on supplements for ME/CFS shows promise but faces significant limitations.
Studies typically involve small sample sizes (under 100 participants) with design issues including bias risks and short follow-up periods.
Standardization problems persist across studies, with inconsistent diagnostic criteria, symptom measurements and supplement protocols.
Publication bias favors positive results, while adverse effects and dropout rates often go unreported.
A 2017 systematic review concluded there is “insufficient evidence” for nutritional supplements and dietary interventions for ME/CFS, highlighting these methodological weaknesses.
Future Research Needs
- Larger studies with more patients
- Standard diagnosis and measurement methods
- Longer follow-up periods
- Research on which patients benefit from specific supplements
- Investigation of combination supplement approaches
Takeaway
The research on supplements for ME/CFS shows mixed results.
Some supplements look promising, including CoQ10 with NADH, NAD+ precursors, L-carnitine, and creatine. However, research limitations make it hard to draw firm conclusions about most supplements.
The quality of evidence varies greatly, and no single supplement works for all ME/CFS patients.
If you have ME/CFS and want to try supplements, work with healthcare providers who understand your condition. Focusing on supplements that address your specific deficiencies or symptoms may lead to better results.
Scientists must continue conducting careful research to learn which supplements truly help ME/CFS patients and how they work. This research is essential for developing better treatments.
Remember that supplements might ease symptoms but cannot cure ME/CFS. Always work with knowledgeable healthcare providers to develop your full treatment plan.
Referenced Sources
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5409455/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10816159/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4346380/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5010273/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11819863/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7442590/ ↩︎
- https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpendo.00242.2023 ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10071523/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9116917/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15039515/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15072869/ ↩︎
- https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/application-summaries/research-summaries/creatine-and-brain-function-in-cfs/ ↩︎
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/19/3308 ↩︎
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/fsn3.3597 ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28059425/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25210673/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22677357/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34027128/ ↩︎
- https://www.trialx.com/clinical-trials/listings/274122/melatonin-and-zinc-administration-on-cardinal-symptoms-in-myalgic-encephalomyelitischronic-fatigue-syndrome/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28755683/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8151278/ ↩︎